A recent study published in the Annals of Oncology painted a grim picture for men who had five or more partners with whom they engage in oral sex. These men were shown to have the highest risk of developing a type of head and neck cancer (oropharyngeal cancer) that is triggered by exposure to the human papilloma virus – known as HPV.
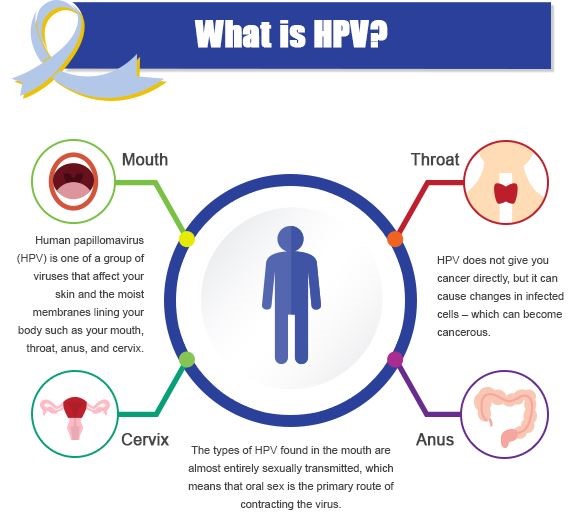
HPV, the most common sexually transmitted disease in the United States, is responsible for approximately 70% of all oropharyngeal squamous cell cancers (OPC). Moreover, the incidence of HPV-related OPC (HPV-OPC) among men has more than doubled over the past 20 years. While risk of infection among men is high, actually having it develop into cancer is still low.
According to the study, “Only 0.7% of men will ever develop oropharyngeal cancer in their lifetimes. The risk was much lower among women, anyone who did not smoke, and people who had less than five oral sex partners in their lifetimes.” (HPV in women is strongly linked to cervical cancer.)
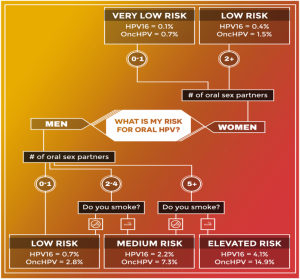
Other risk factors include smoking and drinking. Eighty-five percent of head and neck cancers are linked to smoking. Alcohol abuse also increases the risk of head and neck cancer.
Symptoms may include trouble swallowing; a sore throat that lingers; inability in moving the tongue or mouth fully; ear pain and/or a lump in the back of the mouth, throat, or neck. If diagnosed in its early stages, it is fully treatable.
If you suffer with any of the symptoms above, make sure you contact your doctor.
Strategic Communications Professional/Content Strategist/Marketing Communications Consultant